IBM Database Family
IBM rebranded DB2 as Db2. Therefore, both database names refer to the same database.
Db2 is a Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) originally introduced by IBM in 1983 to run on its MVS (Multiple Virtual Storage) mainframe platform. The name refers to the shift from the then prevalent hierarchical database model to the new relational model. Although Db2 was initially designed to work exclusively on IBM mainframe platforms, it was later ported to other widely used operating systems like UNIX, Windows, and presently in Linux. Db2 is an integral part of IBM’s information management portfolio. It is a full-featured, high-performance database engine capable of handling large quantities of data and concurrently serving many users.
Formerly known as Db2 for Linux, UNIX and Windows is a database server product developed by IBM.
Db2 LUW is the "Common Server" product member of the Db2 family, designed to run on most popular operating systems.All other Db2 products are specific to a single platform.
Best practises of IBM Db2 or Db2 in this article refer to IBM Db2 for Linux, Unix and Windows product only.
Db2 for z/OS is a relational database management system that runs on the mainframe.
Latest version is Db2 12 for z/OS.
Db2 for i is an IBM i integrated Relational Database Management System that leverages the high performance, virtualization, and energy efficiency features of IBM Power Systems.
The IBM® Integrated Analytics System consists of a hardware platform and optimized database query engine software that work together to support high performance data analysis and business reporting features.
As illustrated by IBM Document, the IBM® Integrated Analytics System uses Db2® Warehouse which runs in a Docker container as data and analytics applications.
According to IBM product hub, Db2 Warehouse is an analytics data warehouse based on containerization technology and Db2 engine.
Latest Db2 engine for Db2 Warehouse is Db2 11.5.4.0 engine(till 30 June 2020).
Db2 Warehouse can be deployed two ways:
Key feature of this products are list below:
Netezza Performance Server (NPS), previously named IBM Performance Server for PostgreSQL (IPS), is an optional service (add-on) data warehouse solution.
It is built on IBM Red Hat OpenShift and is optimized for High Performance Analytics.
It can be deployed:
Netezza Performance Server is based on the same code as previous generation Netezza appliances (IBM PureData System for Analytics), so the solution is fully compatible with these appliances. Any existing Netezza scripts and SQL applications can be run without modification on Netezza.
You can refer to IBM Knowledge Center for detailed information.
Product | Version | Release Date |
|---|---|---|
Db2 for Linux, UNIX, and Windows | 11.5.5.0(11.5 Mod 5 Fix Pack 0) | Nov 18th, 2020 |
Highlights
Product | Version | Release Date |
|---|---|---|
Db2 for IBM i | 7.4 TR3(IBM i 7.4 Technology Refresh 3) | Nov 13th, 2020 |
Highlights
Type Model | VRM | Announced | Available | Marketing Withdrawn | Service Discontinued |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
5650-DB2 | 12.01.00 | 2016-10-04 | 2016-10-21 | - | - |
5615-DB2 | 11.01.00 | 2013-10-01 | 2013-10-25 | 2018-07-02 | 2021-03-31 |
5615-DB2 | 11.00.00 | 2012-10-03 | 2013-03-08 | 2013-10-25 | - |
Highlights
Product | Version | Release Date |
|---|---|---|
IBM® Integrated Analytics System | 1.0.24.0 | November, 2020 |
Highlights
Product | Version | Release Date |
|---|---|---|
Netezza Performance Server | 11.2.0.0 | December, 2020 |
Highlights
MicroStrategy rebrand Progress Data Direct drivers and shipped then out of box for Db2.
IBM Db2, IBM Db2 for i, IBM Db2 for z/OS, IBM Db2 Warehouse share the same ODBC and JDBC Driver in MicroStrategy products, but connection parameters may be different. You can refer to official driver document for correct connection parameters.
MicroStrategy support IBM Netezza, but does not ship any Netzza drivers. Native drivers can be installed in MicroStrategy products.
Key features of MicroStrategy shipped driver for IBM Db2:
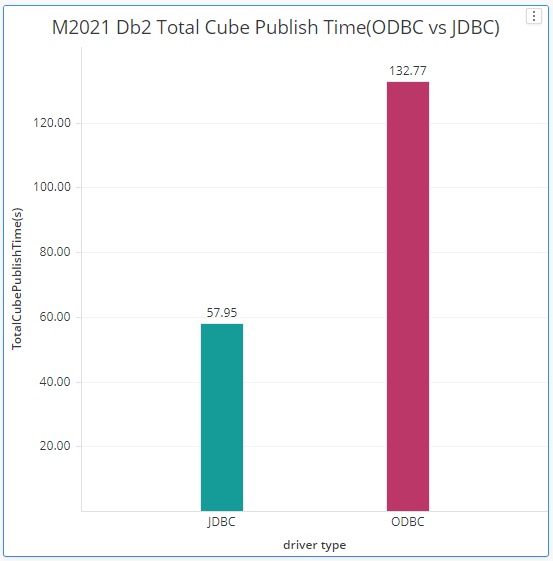
For IBM Db2, both ODBC and JDBC drivers are shipped out of the box with MicroStrategy. From the results of single cube publish testing which records and compares the time spent for a single cube (4M rows) republish, JDBC driver has better performance than ODBC driver.
Shipped driver refer to Data Direct driver which installed along with MicroStrategy Intelligence Server
Native driver refer to IBM Data Server Driver for ODBC and CLI (64-bit)
Based on our single cube push test, Native ODBC Driver and shipped ODBC Driver have similar performance.
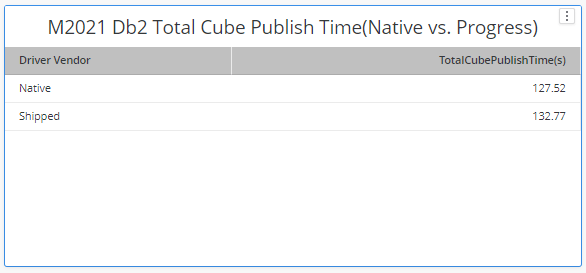
It’s suggested to use shipped drivers in regular use cases to get a more integrated and thorough support since we have fully certified shipped driver from all aspects including connectivity, functionality, security.
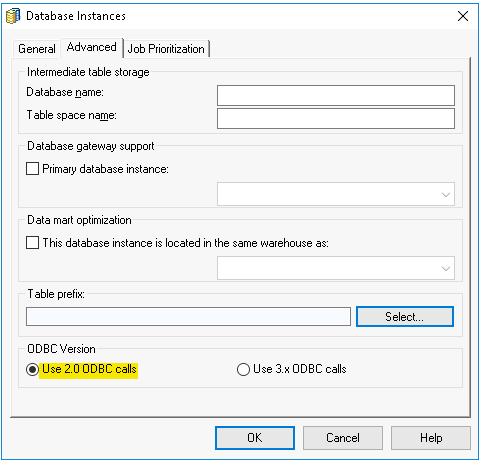
Customer can change ODBC version in the MicroStrategy Database Instance level, as described in below:
Select the database instances, right click, in bottom of the Advanced tab, tick Use 2.0 ODBC call.
Click Modify the database connection, in the Advanced tab, tick Use extended fetch. By default, extended fetch is automatically enabled in ODBC call 3.x, while ODBC call 2.0, you need to manually enable extend fetch in Database Instance.
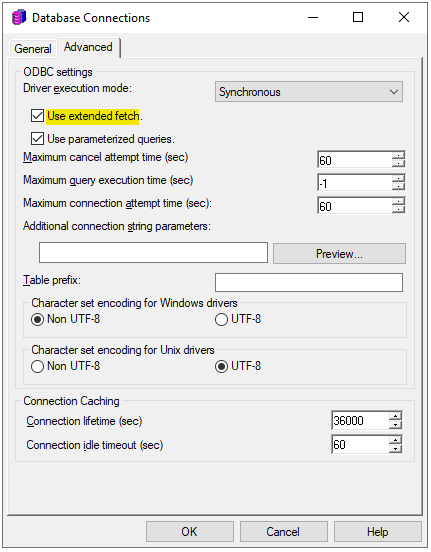
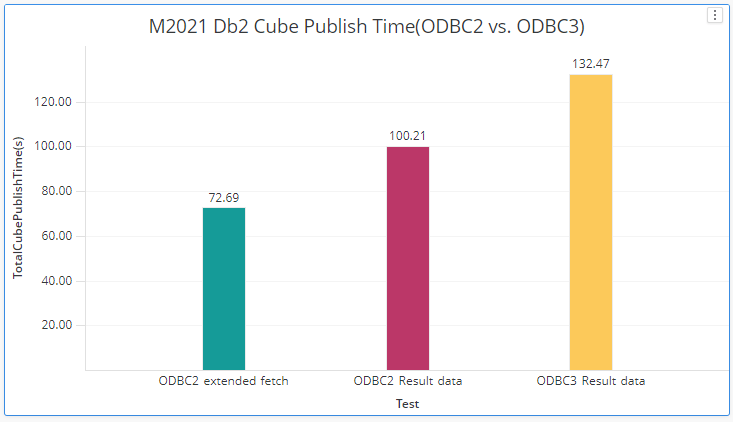
Based on single cube publish testing, for shipped driver, ODBC version 2 has better performance than ODBC version 3, while ODBC call version 2 with extended fetch has the best performance of above. But for Benchmark test with concurrent user, ODBC version 2 or with extend fetch do not show performance advantage compared to ODBC version 3.
Latest Driver Version from Progress(till 1/7/2021):
Current Version in MicroStrategy:
Failure Number | Driver | Driver | Bas | Utl | Flt | Java jar Component | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
XDBC-26651 | DB2 | 0385 | B0566 | U0411 |
|
| When attempting to insert data into a column of Timestamp type in DB2 iSeries database, <br/>the driver returned the following error: "[ODBC DB2 Wire Protocol driver][UDB DB2 <br/>for iSeries and AS/400]STRING REPRESENTATION OF DATETIME VALUE HAS INVALID SYNTAX." |
XDBC-24993 | DB2 | 0385 | B0566 | U0411 |
|
| After the database failover due to Idle thread timeout, the driver failed to execute <br/>prepared statements in the new connection. |
XDBC-25810 | DB2 | 0381 | B0564 | U0410 |
|
| For an application hosted in IBM cloud, when attempting to execute a parameterized SQL <br/>query with a LIKE clause, the driver returned an empty result set. |
XDBC-25458 | DB2 | 0381 | B0564 | U0410 |
|
| The ODBC-DB2-bind27 executable crashed while creating the DB2 bind packages. |
XDBC-25356 | DB2 | 0374 | B0558 | U0406 |
|
| When the driver attempted to insert duplicate records into a table with a unique constraint, <br/>the job application failed instead an error being returned. |
XDBC-24903 | DB2 | 0376 | 548 | 397 |
|
| When specifying a character set using the Charset option, the driver failed to return <br/>a result set for a Select query that contained non-numeric parameters. |
Patch | Issue | Driver | Driver | Framework | Util | Adapter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0279 | XDBC-21861 | DB2 | 0291 | F000460 | U000218 | The driver failed to connect when the username or password contained special characters. |
Below session describes tuning Db2 for Analytical workload for internal benchmark test. In house environment, we use 32G CPU and 244G memory for Intelligence Server and Db2 Server. The version for the Db2 Server in house is 11.1.4.4 on Linux Platform.
The tuning requires administrative privilege again the Db2 database server.
The tuning is based on Db2 official document to tune Db2 for Analytical Workload: Creating and setting up your database configuration for analytic workloads.
You should tune the sortheap and sheapthres_shr parameters carefully. Under workload of high concurrency, both area will overflow and you will get SQLCODE -955 error when running the report. When you encounter this error, consider adjusting the concurrency via Job Prioritization in MicroStrategy database instance configuration or dft_degree or lower the value of both sortheap and sheapthres_shr
Error type: Odbc error. Odbc operation attempted: SQLExecDirect. [HY000:-955: on SQLHANDLE] [MicroStrategy][ODBC DB2 Wire Protocol driver][UDB DB2 for Windows, UNIX, and Linux]Unknown error: SQLCODE -955 For more information, please consult DB2 document for error code SQL0-955.
With concurrency of 5, the performance can be enhanced up to 38% to 63%. But such configuration have limitations. The error ratio also increases when the number of concurrency is increased, especially when you increased default number of jobs in How to increase number of connections by low priority.
5 Concurrent Threads | Before Analytical Workloads Configured | After Analytical Workloads Configured | Improvement Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
Avg RT(sec) | 2.264 | 1.384 | 38.87% |
Throughput(per min) | 132.51 | 216.76 | 63.58% |
This feature is firstly introduced in M2021 and enabled by default for IBM Db2 gateway.
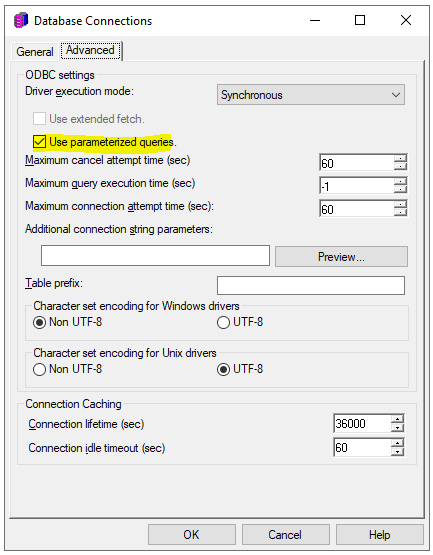
Parameterized queries are SQL queries that can use placeholders for data. Using placeholders allows these queries to be re-used. The following is an example of a parameterized query:
select a12.MONTH_ID MONTH_ID,
MicroStrategy Parameterized Query feature for better performance
With Parameterize Query on, the query can be re-used and the data retrieving performance will be increase by 10% for IBM Db2.
Another common situation with Parameterized Query will be combining multiple inserts of data into the database as a single query. Sample queries generated look like
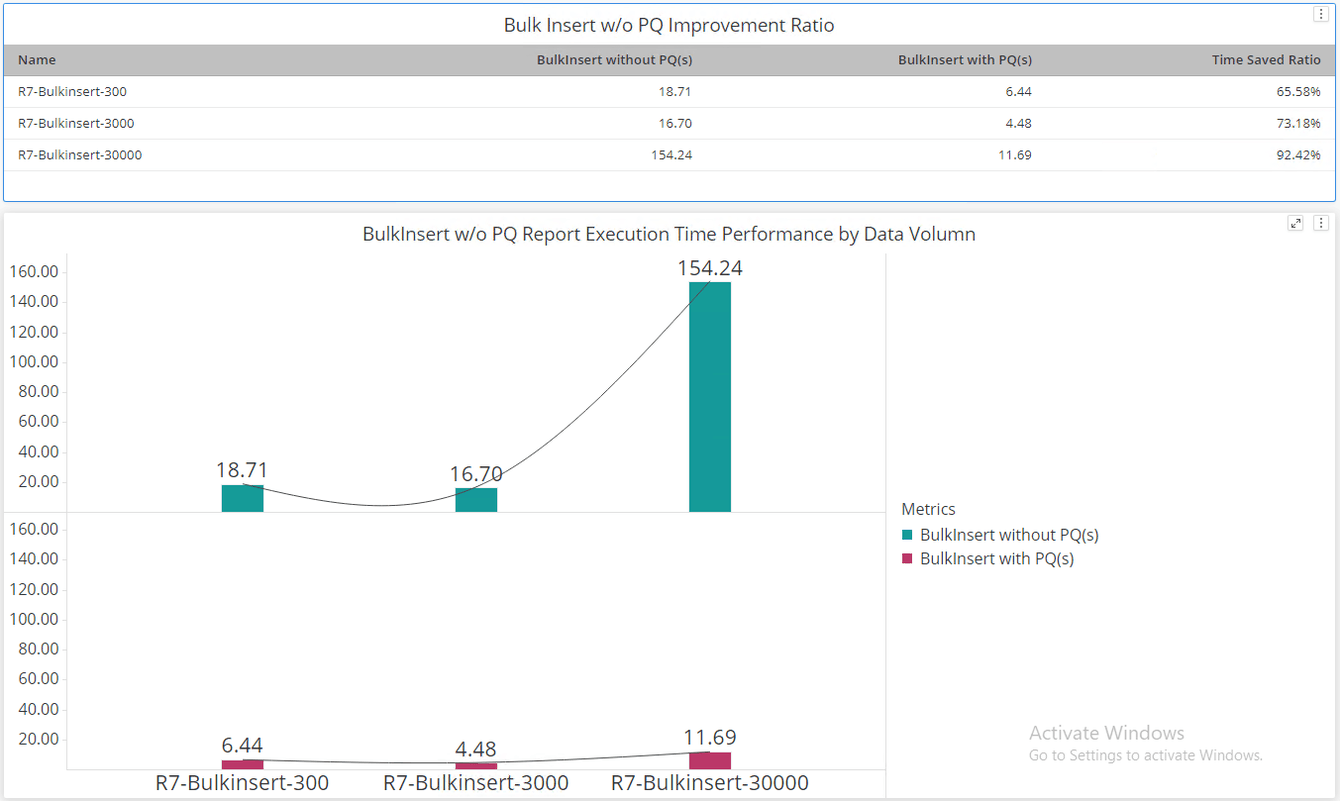
INSERT INTO DMTABLE (Customer_ID, Customer_Name) VALUES (?, ?)Such query combing multiple inserts is called "Bulk Insert". Db2 will benefit from "Bulk Insert" by reusing query plans after turning on the Parameterized Query feature.
For the scenario in below chart, we have created 3 reports that generate insert query with 300,3000 and 30000 rows of data. Compare to base scenario without PQ enabled, running reports with bulk insert query. The targeted scenario with PQ enabled have significant improvement in the report execution time. There is up to 65% - 92% execution time saved ratio in our internal test as illustrated in the chart.
MicroStrategy 2020 introduces a new feature that will apply the correct quotes to all identifiers.
For IBM Db2, double quotation marks "#0" are used in SQL generation, sample SQL will be:
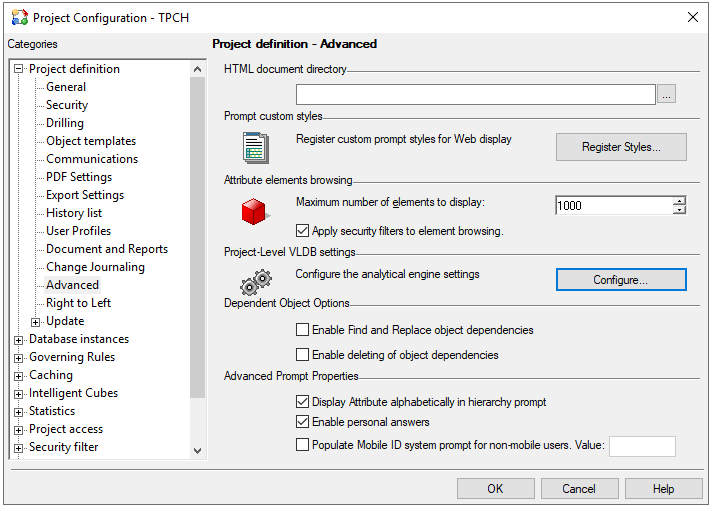
insert into TI9WWF9FSMQ000And in MicroStrategy 2021 we applied an entry in VLDBs for user to turn on/off the quoting feature more visible in developer (under Project Configuration → Advanced → Project-Level VLDB settings → Query Optimizations).
With each product release improvements and enhancements made to the MicroStrategy Analytical Engine can cause minor changes in the data returned when executing dossiers and documents. The default engine version in M2021 is AE13. Details changes could refer to page https://community.microstrategy.com/s/article/Data-Engine-changes-in-MicroStrategy-2021-release?language=en_US
For example, With AE version 12 and above, MicroStrategy push filters down to database for execution in order to minimize the intermediate results set size. This pushdown can significantly improve the performance of dossier execution.For Db2, We did not find any significant improvement.
See page https://community.microstrategy.com/s/article/KB483573-Metric-Qualification-Filter-not-Push-Down-in-ConnectLive-leads-to-performance-degrading for details.
Security considerations of data access are important to MicroStrategy. In below section, we will discuss common technologies of security.
Token authentication is a mechanism for generalizing tokens such that they can be used for authentication in a unified method.
According to IBM Document, starting from Db2 Version 11.5 Mod Pack 4, Db2 supports JSON Web Tokens (JWT).
MicroStrategy shipped drivers(ODBC/JDBC) do not support Db2 token authentication. An internal enhancement request has been raised to driver vendor. Once the drivers support this feature, Certification of the feature will conducted against Db2.
MicroStrategy supports most of traditional authentication, like standard authentication, kerberos authentication, warehouse pass-through as well as windows authentication. You can refer to MicroStrategy Support Document for Db2 for MicroStrategy support of thoses traditional authentications.
Authentication | Standard | LDAP | Kerberos | Warehouse Pass-though | Windows Authentication | User Defined Roles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MicroStrategy Support | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y |
Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol, to enable a client to validate the certificate of a server, and to provide private communication between the client and server by use of encryption. TLS configuration require both server and client configuration. Your system/database administrator may already configured on server side or you can refer to IBM Document for detailed information. For client configuration of MicroStrategy as Db2 client, you can refer to MicroStrategy Support Document for Db2. MicroStrategy use TLS v1.2 by default.
Below tuning suggestion is based on IBM Document on Performance Tuning.
This article will not discuss the hardware recommendations.
Administrative access to the OS is required to modify system parameters.
Recommendation of kernel parameters is based on IBM Document on Kernel Parameters Requirement.
kernel settings in /etc/sysctl.conf
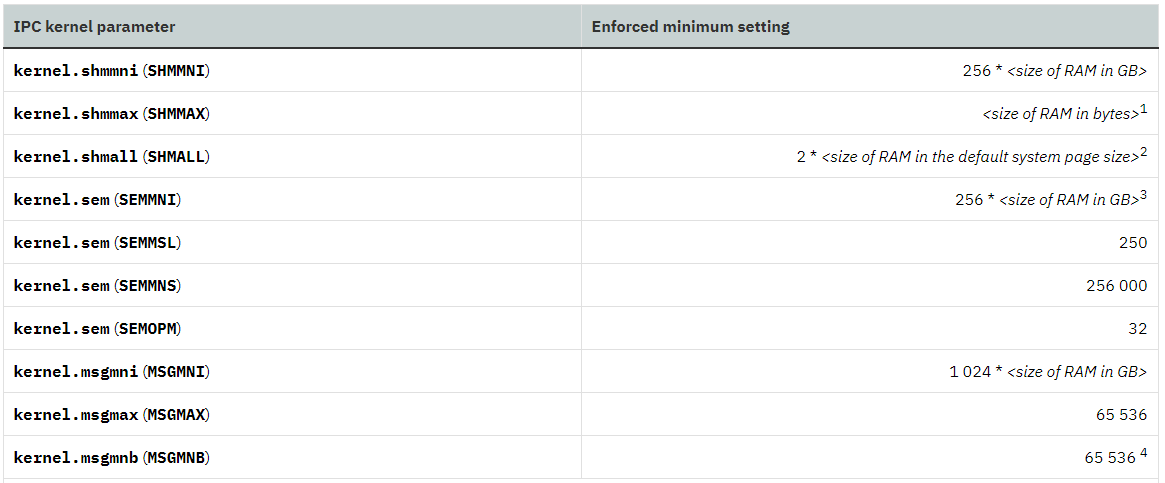
Administrative access to the database is required to modify system parameters.
You can initialized a Db2 database using CREATE DATABASEcommand as listed in IBM Knowledge Center.
Command parameters recommended
Adaptive Self Tuning Memory is also enabled by default for single partition databases.
Enable sort memory tuning
To enable sort memory tuning (sortheap), you must set sheapthres equal to zero in DATABASE MANAGER CONFIGURATION.
Tuning on Database manager shared memory
Below shows how database manager shared memory is allocated, which can be referenced in IBM Document on Database Manager Shared Memory.
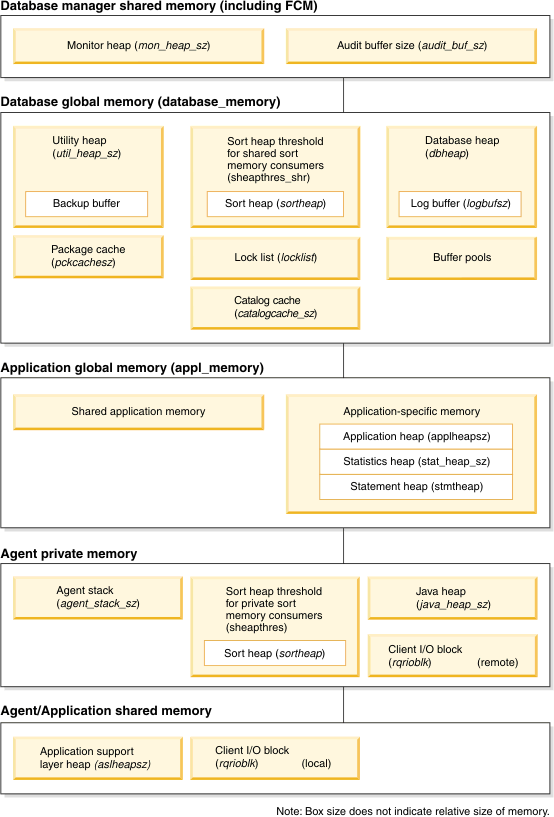
Application Support Layer Heap Size (ASLHEAPSZ)
It is good practice to eliminate the "Rejected Remote Block Cursor requests" completely by monitoring the database and increasing the ASLHEAPSZ parameter until the "Rejected Remote Block Cursor requests" element is zero. And The number of rejected block cursor requests can be determined by using a database manager snapshot.
To set the application support layer heap size, use the following command:
db2 update dbm cfg using aslheapsz 20
Maximum Requester I/O Block Size (RQRIOBLK)
The default maximum requester I/O block size is 32 KB, and the maximum size is 64 KB. The default value is sufficient for most workloads; however, if the size of the application requests and/or result sets generated is greater than 32 KB, increasing the maximum requester I/O block size will result in fewer communication packets being sent back and forth across the network and can result in result sets being returned to the application quicker.
Because DB2 allocates only as much memory as needed, setting the maximum requester I/O block size to 64 KB will not hurt performance but in many cases will help improve performance. To set this parameter to a value of 64 KB.You can use below command to modify the configuration.
db2 update dbm cfg using rqrioblk 65535
Agent stack size(AGENT_STACK_SZ)
If you are working with large or complex data, update the value to a higher value.
You can use below command to modify the configuration.
db2 update dbm cfg using agent_stack_sz 32768The connection concentrator is activated when the number of maximum logical agents is set higher than the number of database agents.
Logical agents (LAs) to handle the application context while database agents (DAs) handle the actual DB2 connections.
DA is disassociated from the LA and is returned to the agent pool when a transaction completes.
connection concentration vs. connection pooling
Normally There is a one-to-one relationship between connections and db2 agents. The connection concentrator permits a many-to-
one relationship between connections and agents.
Setting the appropriate value for this parameter can reduce the cost of continually creating and terminating DB2 agent processes.
Connection concentrator is enabled by setting:MAX_CONNECTIONS>MAX_COORDAGENTS
You can use below command to modify the configuration.
db2 update dbm cfg using MAX_COORDAGENTS 200
Enable Intra-Partition Parallelism (INTRA_PARALLEL)
Intra-partition parallelism should be enabled only if the server has more than one processor (CPU).
You can use below command to modify the configuration.
db2 update dbm cfg using intra_parallel yes
Maximum Query Degree of Parallelism (MAX_QUERYDEGREE)
The maximum degree of intra-partition parallelism specifies the maximum number of subagent processes that any SQL statement can use within the database instance (or database partition, if the database is partitioned). This parameter is effective only if intra-partition parallelism is enabled by setting the INTRA_PARALLEL configuration parameter to YES.
The default value for the maximum degree of intra-partition parallelism is -1, or ANY. This value allows the DB2 optimizer to set the degree of parallelism based on the number of CPUs in the server and the current workload on the server. If a value greater than one is specified, this value will limit the degree of parallelism for all SQL statements executed within the database instance or database partition.
If the value is not -1 or ANY in your environment, please examinate the reason and below command to modify the configuration.
update dbm cfg using max_querydegree any
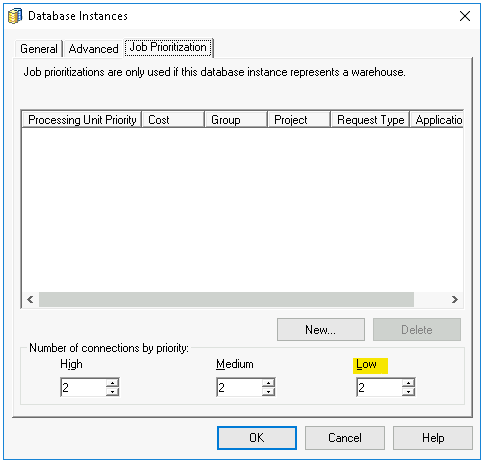
Job Prioritization
Administrators can, based on priority, specify the number of warehouse connections that are required for efficient Job processing. There are three possible priorities for a Job: high, medium and low.
Administrators are not required to set medium and high connections, but must set at least one low connection, because low priority is the default Job priority.
The optimal number of connections is dependent on several factors, however the main criterion to consider when setting the number of connections is the number of concurrent queries the Warehouse Database can support.
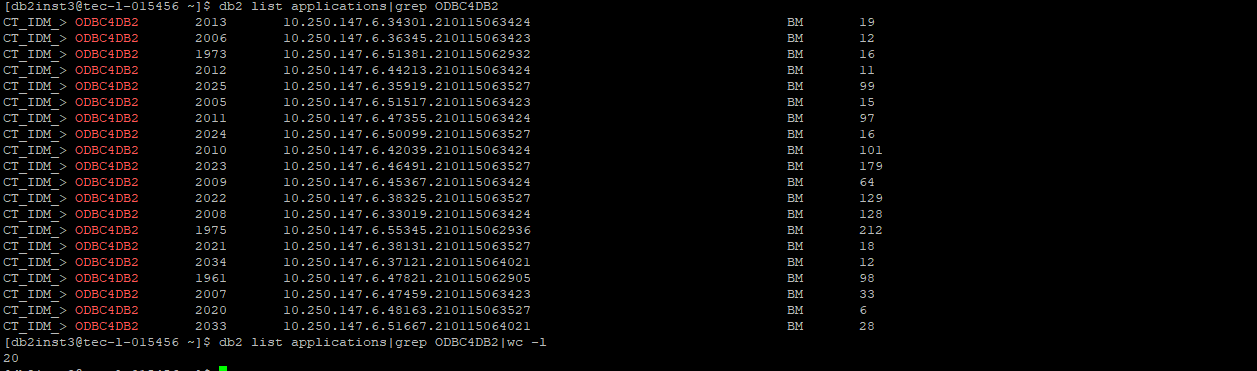
Below is an example from database side if you set Number of connections of low priority to 20. You can see the count of connection in the database side is 20.
Project Level: Right click on project name -> Project Configuration -> Advanced -> Configure
Database Instance Level: Database Instance ->VLDB Properties
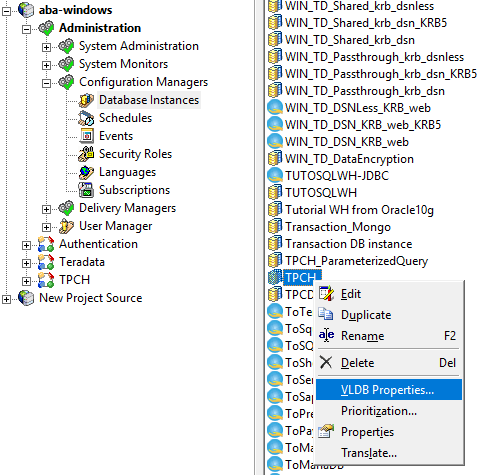
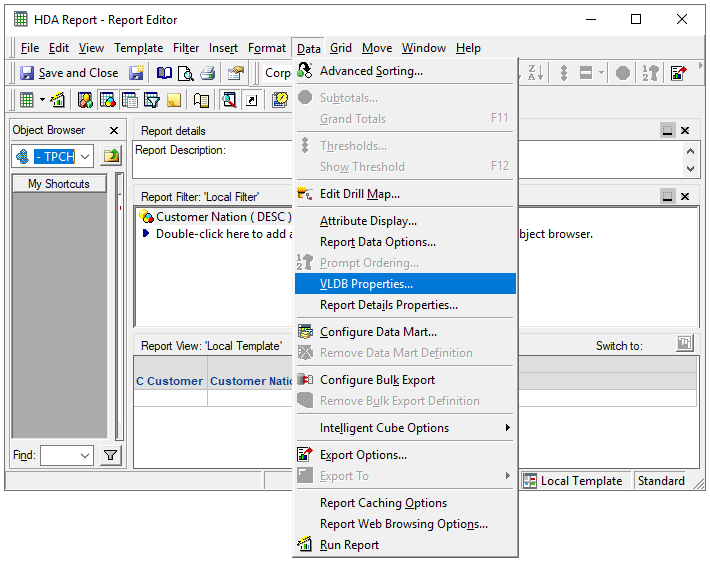
Report Level: Data -> VLDB Properties
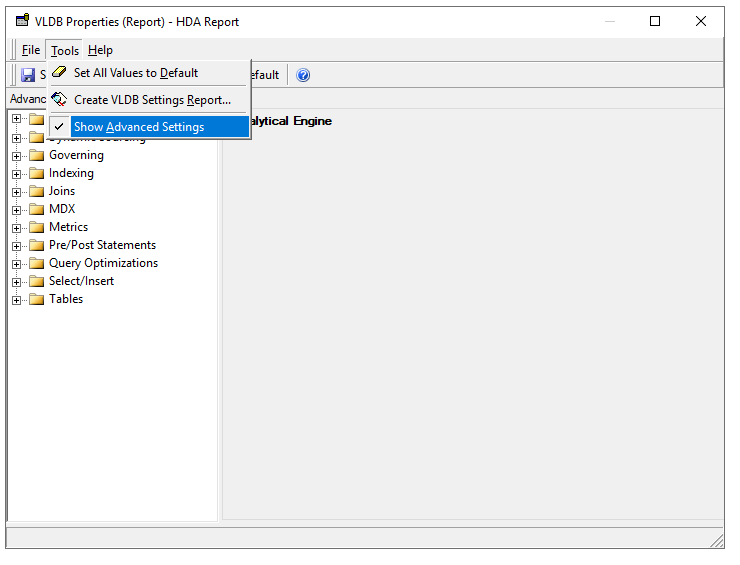
Unhide Parallel Options: Tools -> Show Advanced Settings
The MicroStrategy platform provides VLDB settings for all supported RDBMS platforms to generate optimized SQL that takes advantage of database-specific functionality. See How to Edit VLDB Settings in Appendixes for configuration entrance
SQL Global Optimization
This setting can substantially reduce the number of SQL passes generated by MicroStrategy. In MicroStrategy, SQL Global Optimization reduces the total number of SQL passes with the following optimizations:
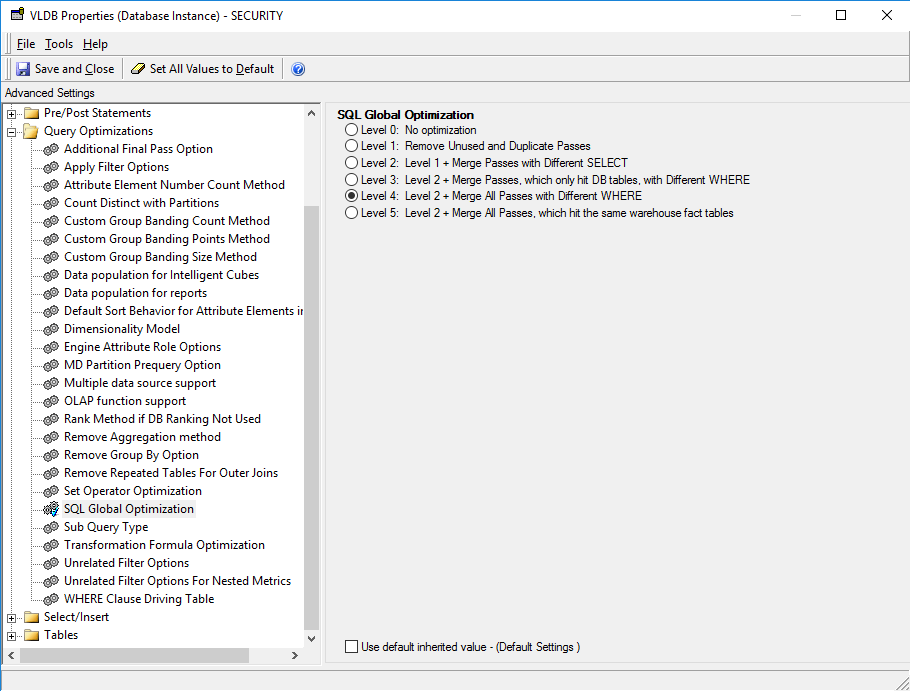
The default setting for IBM Db2 is to enable SQL Global Optimization at its highest level.
Set Operator Optimization
This setting is used to combine multiple subqueries into a single subquery using set operators (i.e. UNION, INTERSECT, EXCEPT). The default value for IBM Db2 is to enable Set Operator Optimization.
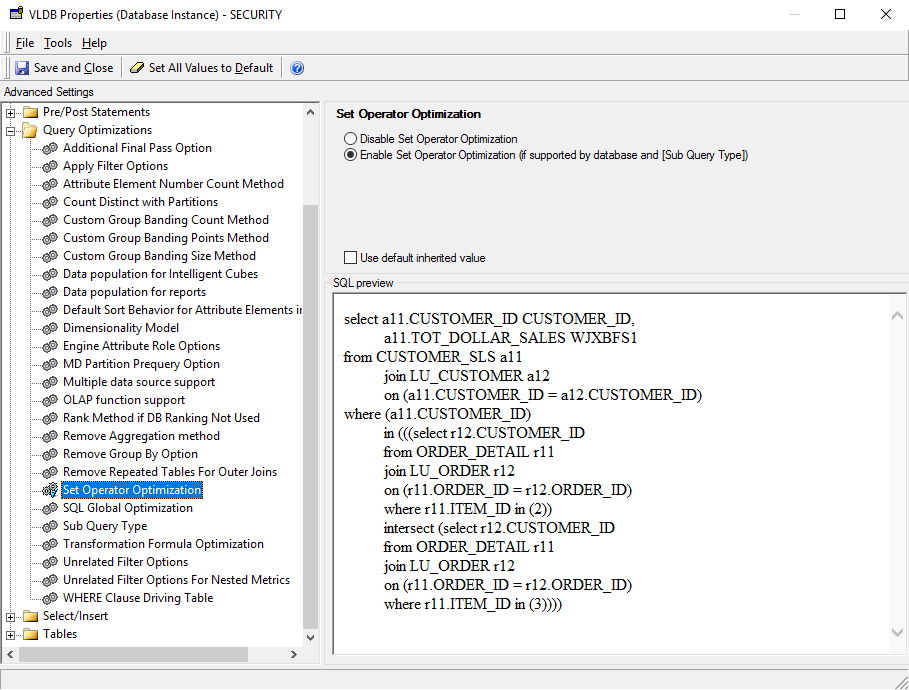
The following is an example SQL command after enabling the setting.
select a13.CATEGORY_ID CATEGORY_ID,Sub Query Type
The default setting for Sub Query Type for IBM Db2 is Option 5 – “Use temporary Table, falling back to EXISTS (SELECT *…) for correlated subquery”.
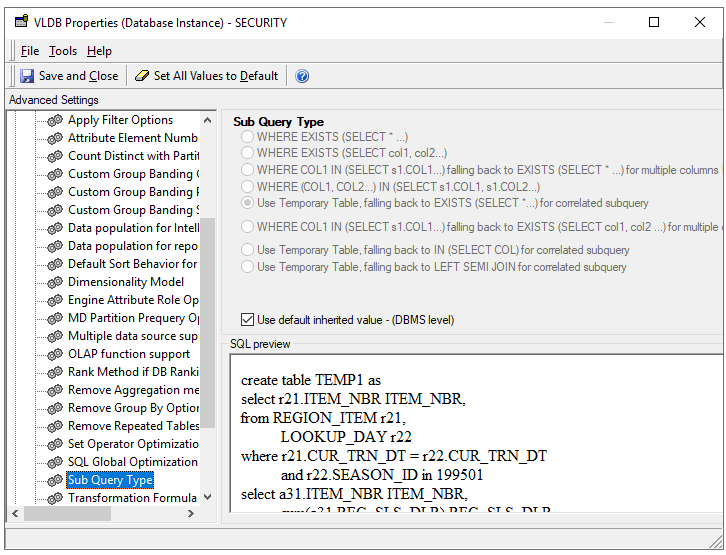
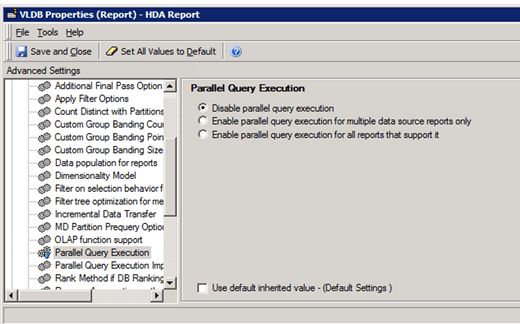
Turn on Parallel Query
The Parallel Query Execution is an advanced property which determines whether MicroStrategy attempts to execute multiple queries in parallel to return report results faster and publish Intelligent Cubes.
Turn on/off the Parallel Execution on project level or report level: Query Optimization -> Parallel Query Execution