If your queries take a long time to execute, you can check the execution plan of the query to see if nested loops are used by executing the Explain analyze %detail query% in the dbquery tool.
In the example below, nestloop is used to scan the access transactions table 259 times, which takes 585 seconds. After disabling nestloop, the same query takes 8 seconds to execute.
Example:
Insert on test (cost=328.07..272870.76 rows=241 width=32) (actual time=585812.907..585812.907 rows=0 loops=1)
-> Subquery Scan on "*SELECT*" (cost=328.07..272870.76 rows=241 width=32) (actual time=24074.355..585810.978 rows=57 loops=1)
-> GroupAggregate (cost=328.07..272865.94 rows=241 width=48) (actual time=24074.352..585810.815 rows=57 loops=1)
Group Key: access_transactions.badge_id, a13.budget_directory_rvp_id, a13.directorate_id
-> Nested Loop (cost=328.07..272859.31 rows=241 width=48) (actual time=19535.913..585771.423 rows=41699 loops=1)
。。。
-> Seq Scan on access_transactions (cost=0.00..270344.50 rows=174769 width=40) (actual time=925.618..2252.541 rows=166981 loops=259)
Filter: ((access_type_id <> 1) AND (facility_id = 287) AND (tran_type_id <> ALL ('{15,5,-1,0}'::integer[])) AND (tran_date_est >= to_date('2016-10-30'::text, 'YYYY-MM-DD'::text)) AND (tran_date_est <= to_date('2016-11-05'::text, 'YYYY-MM-DD'::text)))
Rows Removed by Filter: 3781178
Planning Time: 8.963 ms
Execution Time: 585813.152 ms
There are several ways to disable nested loops.
In the PostgreSQL database, execute the following command to disable nestloop for a specific user. This change applies to all user sessions created by the username you specify.
ALTER ROLE username SET enable_nestloop=off
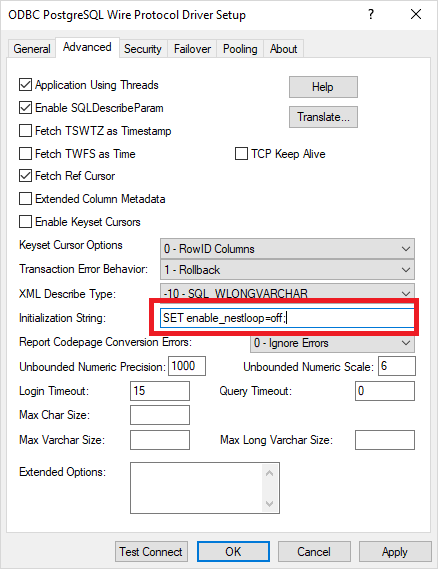
InitializationString=SET enable_nestloop=off DSN Example: [DSN_Progress] Description=Strategy ODBC Driver for PostgreSQL Wire Protocol Driver=/driver_path/MYpsql64.so Database= HostName= PortNumber= InitializationString=SET enable_nestloop=off; ...
ConnSettings=SET enable_nestloop=off DSN Example: [DSN_Native] Description=PostgreSQL Unicode(x64) Driver=/driver_path/psqlodbcw.so Database= Servername= Port= ConnSettings=SET enable_nestloop=off; ...
These changes apply to all connections created by the DSN.