The first step in analyzing the performance of Intelligent Cube Publication is to look at the post-execution SQL view of the initially published Intelligent Cube and understanding the breakdown. Typically, a long duration is seen in the Data Transfer time which indicates the time it takes to fetch data from the warehouse. The data retrieval is dependent on the network bandwidth, but in most Production Enterprise environments, this is not an issue as the network capacity is high enough to handle large volumes of data effectively.
In some instances, the slow down can with the Analytical Engine processing or Other Processing i.e., the post-data fetch operations that need to happen on the Intelligence Server to create the Intelligent Cube data.
Query Engine Execution Start Time: 26-Nov-18 3:02:48 PM ..... Query Generation Time: 0:00:01.07 Total Elapsed Time in Query Engine: 0:00:21.10 Sum of Query Execution Time: 0:00:16.80 Sum of Data Fetching and Processing Time: 0:07:10.07 Sum of Data Transfer from Datasource(s) Time: 0:00:00.06 Sum of Analytical Processing Time: 0:00:00.28 Sum of Other Processing Time: 0:00:04.22 .... .... Number of Rows Returned: 1111224 Number of Columns Returned: 83
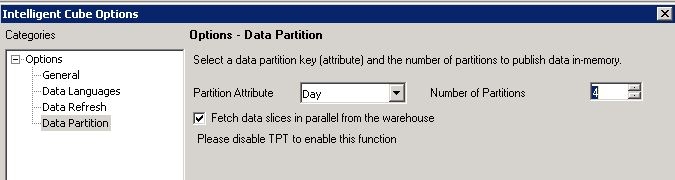
Adjust the VLDB setting Query Optimization > Data Population for Intelligent Cubes
The default normalization option 'Normalize Intelligent Cube Data in Intelligence Server' is not guaranteed to be the best performing setting for all types of data and schema designs. Change this setting to a different option to see if the Intelligent Cube Publication performance can be improved. If applicable to the specific cube design and schema, modifying this setting can help improve the data retrieval speed and the post-data retrieval operations. For guidance on the best setting that applies to each environment, refer to the following Strategy Community Article:
KB32010: What are the Data Population VLDB properties in MicroStrategy Engine?
Adjust the MaxCrossProcessTableSize
The MaxCrossProcessTableSize setting controls the amount of data transferred between the Strategy Intelligence server and the database process layer.
This setting is applied at the Intelligence server level. The default value is 300 MB, with a maximum value of 4096 MB (4 GB).
Administrators can adjust this setting to potentially increase the speed of data transfer by, for instance, doubling the initial value and observing the results.
However, Strategy does not advise that you increase this setting excessively, as it may lead to performance deterioration.
For more information about this setting, see: KB17628: How to change the maximum database table chunking size used for data transfer between the database multiprocess component (M8MulPrc) and MicroStrategy Intelligence Server
Increase the Rowset size
The
ROWSET_SIZEdetermines the number of rows in a rowset. The Intelligence server uses the MaxCrossProcessTableSize setting and database column size to calculate how many rowsets should be fetched in one round. The Intelligence server fetches at least one
ROWSET_SIZEof rows in a single round.
ODBCConfig.inifile. This file is located in the installation directory on Linux installations and in the
Common Files/Strategyfolder on Windows installations.
ODBCConfig.inifile contains sections for different types of databases. For example, the configuration for a SQL Server database includes sections for ODBC 2.0 and ODBC 3.x Strategy versions 9.4.x and above use ODBC 3.x.
ODBCConfig.ini:
<DB_SECTION ID="300">
<DATABASE>SQL SERVER</DATABASE>
<ODBC20>
<ROWSET_SIZE>160</ROWSET_SIZE>
</ODBC20>
<ODBC35>
<ROWSET_SIZE>160</ROWSET_SIZE>
<PARAM_QUERY_ROWSET_SIZE>32768</PARAM_QUERY_ROWSET_SIZE>
<SCROLLABLE_CURSOR>DEFAULT</SCROLLABLE_CURSOR>
</ODBC35>ODBCMaxLongVarSizeis considered as the max precision of data and can dramatically impact cube publishing performance. It can be defined in the registry file.
ODBCMaxLongVarSizein the DATABASE.PDS.
<PROPERTYSET NAME="VLDB Data Type">
<PROPERTY NAME="Maximum Var Size" VALUE="4000" />
</PROPERTYSET>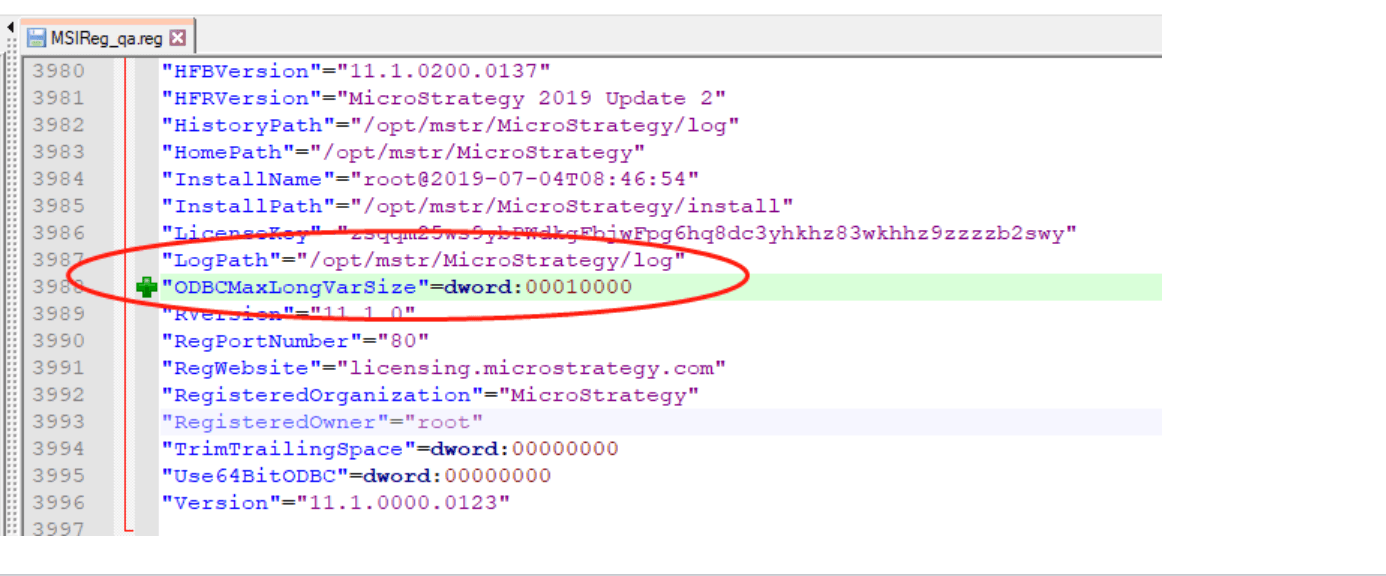
Increase the Fetch size for ODBC or JDBC data retrieval
Most ODBC/JDBC drivers across various data sources have properties such as ArraySize and FetchSize that determine the number of rows fetched in a single network round trip. Administrators can adjust these parameters to optimize performance.
ODBC
The default fetch size for ODBC connections varies depending on the ODBC driver used and the driver-specific properties, which differ across databases.
For instance, in the Oracle ODBC driver, the
ArraySizeproperty specifies the number of bytes the driver can fetch in a single network round trip. Larger values increase throughput by reducing the frequency of data fetches across the network, while smaller values improve response time by minimizing delay. The default
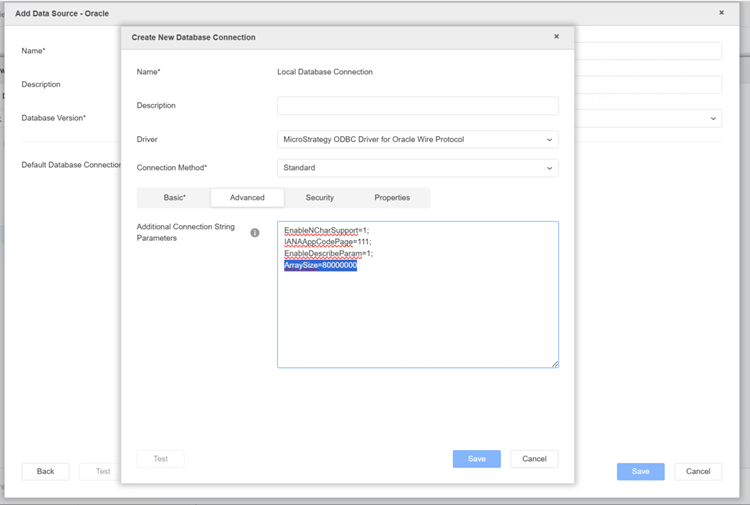
ArraySizein the Oracle ODBC driver is 60000.
ArraySize=80000000to the Oracle ODBC connection string.
Similar optimizations can be made for other drivers with properties like
Fetchfor PostgreSQL and
MaxRespSizefor Teradata.
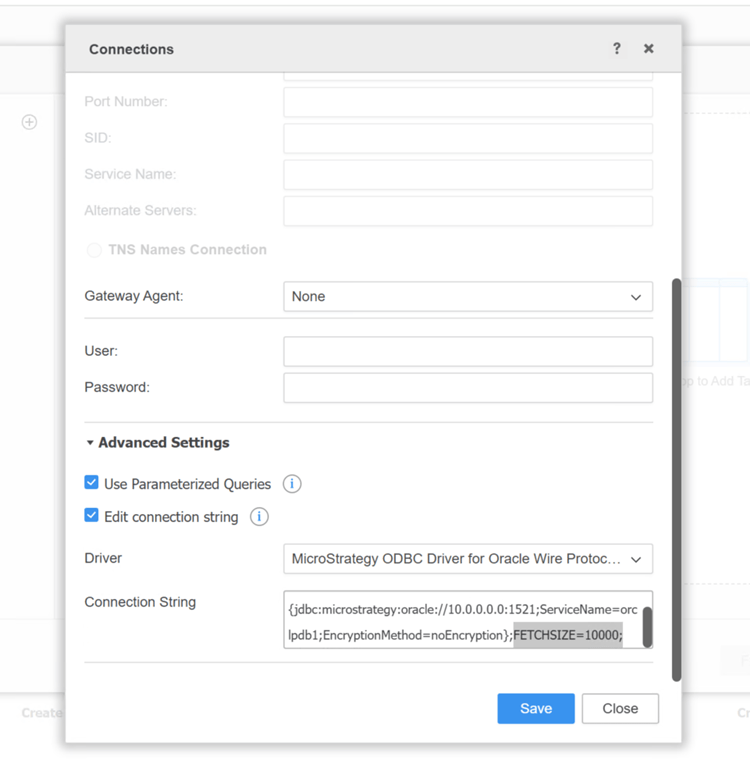
FETCHSIZE=xxxparameter to the connection string of a dbrole, as shown below. This parameter serves as a hint to the JDBC driver and must be supported by the specific driver in use. Some drivers may ignore it if not implemented.
To improve data fetching performance for JDBC connections, administrators can also increase the JNI Bridge Heap Space. For detailed instructions on how to adjust this settings, refer to the following article: KB439951: How to set the maximum Java Heap Size value for JDBC source connectivity in MicroStrategy Developer and Web 2021.
KB442307